Electricity network is the base for our technology world. They distribute necessary energy for electronic equipments in our homes, data processing centers, industry and even remote places where mobile network antennas are installed. Additionally fiber optics are deployed together with electricity cables in towers and pipelines. These fiber optics are used by operators for mid and long distance connections.
Currently electricity networks are in a kind of revolution with “SmartGrid” technology deployment. Electricity production cost is changing continuously depending on the day of the year and even the hour of the day. As an example, during night, production cost is really low compare with during the day when production cost use to be higher. In the opposite side consumption control is done manually checking measurement equipment every one or two months.
SmartGrid technology solve this misalignment between electricity production and consumption control. Thanks to impressive development of data network now it is possible a data connection in each electricity supply point. Measurements equipments are called “SmartMeters” controlling consumption in real-time.
We will revise below most important concepts of electricity networks.
Electricity Network Architecture
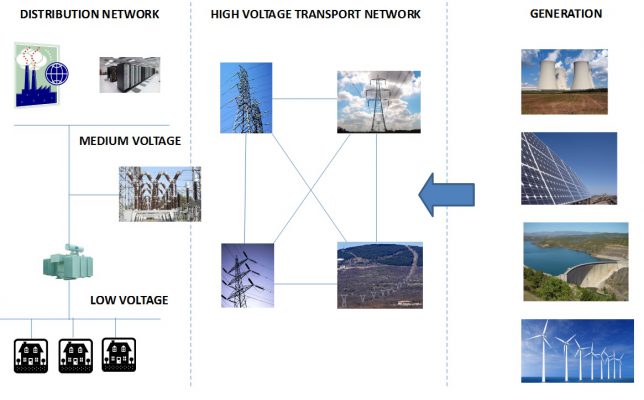
Electricity Generation
Electricity generation includes all plants generating electric energy and supplying to high-voltage transportation network. There are several types of plants:
- Renewable: Renewable plants are hydroelectric, wind and solar ones. They are the most flexible ones adapting their electricity production to current needs. They are cheap and unlimited. The only problem is their capacity depends on not controlled sources like rain, wind or sun.
- Fossil: Fossil plants use coil (highest pollution), diesel or natural gas (lowest pollution). They are quite flexible for adapting to consumption changes. Inconveniences are pollution and a changing fuel price.
- Nuclear: Not too flexible as it takes some days to increase or reduce electricity production. So adaptation to changes in electricity consumption is really poor. It generates no pollution is it is quite secure but the few accidents occurred in the past were really serious.
Usually they are different kinds of them in a country as every type have advantages and disadvantages.
Transformer
Transformer is a key element in an electricity network. Transformer adapt electricity voltage to the right one in order to minimize energy losses. High-voltage transformers are the biggest and they are usually installed outdoor. Medium and low voltage ones are smaller and they are usually installed indoor and sometimes underground. Anyway outdoor installation is used in some cases.

High voltage network
High voltage is the best way to transport electric energy through long distances. High voltage is some hundreds of thousands volts reducing current in the same way. Ten times more voltage means ten times less current and losses are directly proportional to current. High-voltage network is a mesh with several ways between two points. It is possible to interrupt one way because of failure or maintenance without interrupting electricity supply.
Current trend is to connect high-voltage network of several contiguous countries in order to use electricity from the cheapest plant. So electric energy could be used thousands of kilometers from the plant it is generated.
Distribution network
High-voltage network is the best way to transport electric energy but it is clearly dangerous to be used directly by end users and dangerous as well for the buildings next to the network cables.In the border of towns and cities there are transformers reducing voltage to 10.000 volts. This voltage is called medium voltage and it is used to distribute electric energy in a more secure way. Some industries or factories connect to medium voltage distribution network which is useful for big machines.
For most of end-user it is needed to reduce voltage to a more suitable 220 or 120 volts depending on the country. This voltage is called low voltage and it is the usual voltage for most end users. In order to reduce losses medium to low voltage transformers are located next to end users. A small building sometimes underground is built for installing this transformer inside. Outdoor installation, usually in a highest position in a tower, is not the preferred option.
Energy is measured in some points in the network but the most important measurement point is at end-user premise. This measurement point is the one used for billing and distribution company is in charge of manage and maintain it. Distribution company provides individual and aggregated consumption information to the rest of network shareholders. Aggregated consumption should match consumption in other points of the network. Mismatches mean problems like leakage, fraud, equipments broken, etc. Distribution company is in charge of solving these problems. Currently technology for this measurement point is evolving to SmartMeter technology.
Electricity network management
A key factor in an electricity network is energy can not be stored. Production plants should produce the same energy is consumed. No more, no less. As consumption is uncontrolled electricity production should adapt to consumption in real-time.
Frequency use to be 50 Hz or 60 Hz depending on the country. Decision between 50 Hz and 60 Hz was done in each country for different historic reasons and it use to be the same than countries around. It is not possible to connect two networks with a different frequency.
Network manager controls network frequency and compares it with a pattern frequency. This patter frequency use to come from an atomic clock in most countries. If frequency is highest than pattern it means there is more production than necessary and it is needed to “switch off” some plant (or part of it). In the opposite, if frequency is lower than pattern, it means there is less production than necessary and it is needed to “switch on” a plant (or part of it). Usually network manager has a plan based on predicted consumption. Consumption pattern is similar from one day to the following day and only small adjustments are needed .
Network manager criteria use to be the following:
- Nuclear plants never change and their production is adapted to long-term consumption changes.
- Solar and Wind plants are always producing energy if possible as they produce the cheapest energy.
- Fossil plants are more expensive and generate pollution. They have low priority for connecting to the network. Anyway they takes hours to switch on and they are no valid for unexpected fast changes in consumption.
- Hydroelectric plants are the most flexible and their turbines start and stop in less than one hour. Some of them are reversible spending energy from the network and sending water to the upper side of the dam. It uses to be done when there are too much energy in the network because of plants cannot be stopped.
- The last option, if previous steps have failed, it is possible to disconnect some industrial customers or specific areas if there is not enough production.
Network manager use to be a company belonging totally or partially to country government.
SmartMeter
SmartMeter is the base for SmartGrid technology. They control and register electricity consumption and this information is available in real-time both by distribution company and end-user. Both can read current and historic consumption any time. Additionally it is considered renewable sources of electricity like solar panels installed at customer premises. SmartMeter differentiate if the flow is from the network to the customer or vice versa. SmartMeter control the quality of electricity produced by customer as low quality customer equipments could affect other customers.

Methods used to connect SmartMeters to distribution company server are mainly two:
- Mobile networks: Distribution company contract with a mobile operator SmartMeters connection. Every one has a modem (usually only 2G) and a SIM card. Mobile operator offer a really competitive price as the contract consider millions of connections and data traffic is really small.
- Using their own network: Every SmartMeter connects with a concentrator using PLC technology. This concentrator is located next to medium-low voltage transformer. Most of distribution companies have a private TCP/IP data network connecting all sites up to medium-low transformers based on fiber optics deployed with electricity cables.
SmartGrid
SmartGrid technology will provide two dramatic changes in electricity network:
- End customer could be not only consumers but small producers. Installing solar panels they can produce electricity during the day and consume during the night. Electricity company will pay for the KWh sent to the network reducing the bill. The name for this procedure is “net balance” and it is a key factor for renewable energy.
- New tariffs more adapted to the real energy cost. Customer could spend more energy when it is cheaper and less when the energy is expensive. As an example, in some countries with lot of Wind plants, electricity is cheaper in windy days and electricity companies could offer a cheaper prices for consumption in these days. This flexible tariffs are a key factor to optimize energy production.
In order to fulfil these two requirements it is needed an accurate and real-time control of electricity energy flow. SmartMeters are in charge of this control.
